Consumer Rights
|
Definition of Consumer |
A ‘consumer’ is:
|
|
Consumer Goods |
Consumer guarantees applying to goods include:
Consumer guarantees applying to services include:
|
|
Safety |
Also sets out rules for liability for safety defects |
Business Rights
Unfair Contract Terms | Unfair contract terms are those which:
Unconscionable conduct
|
Advertising
Misleading and Deceptive Conduct | Businesses should not make statements which are false or inaccurate – need to be capable of substantiation Puffery is not considered misleading |
Pricing
Price-fixing is prohibited under cartel conduct and prevents businesses colluding to set prices.
Anti-competitive Conduct
“Competition” is not a defined term in the Act, but generally requires that a market reflects the forces of supply and demand.
Whether parties compete depends on the market.
“Market” is defined by the Act to mean a market where goods/services are substitutable for or otherwise competitive with each other.
Substitution means there is cross-elasticity of demand and supply (how a good’s price changes in response to that of other goods). It is determined by:
- Product
- Geography
- Functional level
- Time
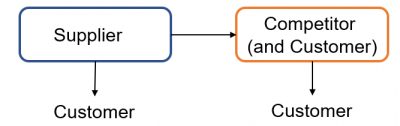
Competitors are Suppliers which supply to Customers in the same market, but may also be Suppliers and Customers to each other.
Types of Anti-competitive Conduct | |
Per se | Regarded as intrinsically anti-competitive, regardless of actual effect. |
Substantially lessening competition | Conduct which has the purpose of or is likely to have the effect of substantially lessening competition
|
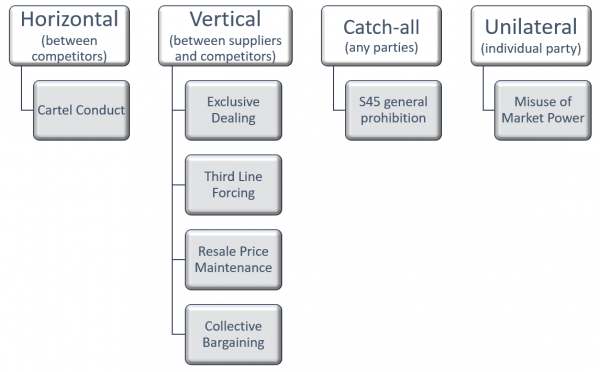
Horizontal Arrangements | |
Cartel Conduct |
|
Vertical Arrangements | |
Exclusive Dealing | Supplying goods or services on the condition that the person doesn’t deal with another supplier, and this substantially lessens competition in the market |
Third Line Forcing | Supplying goods or services on the condition that the consumer also purchases another party’s products, and this substantially lessens competition in the market |
Resale Price Maintenance |
|
Collective Bargaining | Businesses agree to negotiate together with supplier or customer. However, ACCC can provide exemptions where this is in the public interest e.g. small businesses negotiating with big players |
Catch-all Provisions | |
s45 | Conduct not captured by a specific provision, which has the purpose or likely effect of substantially lessening competition. Intended to cover informal communications and cooperation with competitors. |
Unilateral Conduct | |
Misuse of Market Power |
|
Mergers
Mergers are prohibited which have the effect or would be likely to have the effect of substantially lessening competition
