Decisions in Financial Management
Liquidity | Cash flow management |
Investment | Whether and when to invest in which assets |
Financing | Structure of funds – debt/equity |
Profit distribution | Dividends |
Types of Financial Management
Liquidity/working K management | Monitoring of current asset and current liability ratios to ensure sufficient cash flow |
K investment – budgeting | Investment Decision Invest if NPV > 0 i.e. projected earnings > costs i.e. profitable Today’s value of future cash flows – today’s outlay |
Financing – K structure and funding of investment | Financing Decision Debt or equity D/E ratio Gearing: Debt/assets |
Dividends or retain profits | Based on dividend policy (retain earnings or provide dividends, what amount and frequency) |
1. Investment Decision

A. Present Value
NPV: Difference between discounted capital inflows and outflows. Future value is discounted for risk and time value of money.
Time Value of Money: A dollar today is worth more than a dollar tomorrow due to the returns you can earn on it over time.
PV: present value of net future cash flows. The profit a project generates in today’s dollars.
Net: Difference between capital inflows and outflows.
Even if one project has greater returns, another may have a higher NPV if the returns are generated sooner.
Invest if NPV > 0
Excel formula:

B. Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
IRR is the required discount rate/ rate of return that causes NPV = 0.
Compare this with a company’s target rate / minimum acceptable rate of return and IRR of projects with same duration.

C. Breakeven Analysis
The break even point is:
- the time in years at which positive cash flow = negative cash flow
- the unit sales where revenue = total costs i.e. no profit or loss is made
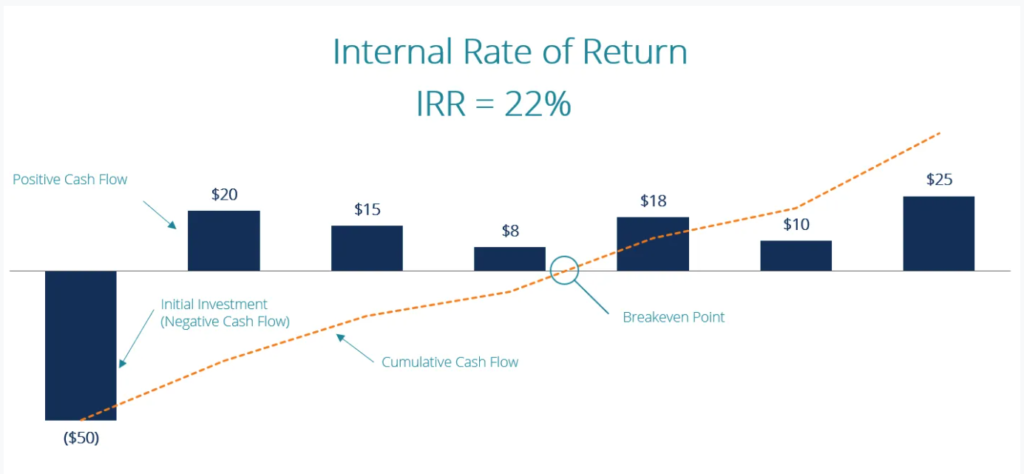

D. Payback
The payback period is the time taken to recover the investment / reach the break even point i.e. pay back the cost.

D. Other methods of investment evaluation
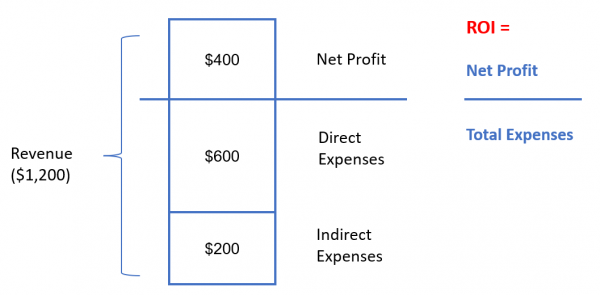
BCR: Benefit Cost Ratio
Accounting Rate of Return (ROI)
Profit / Investment
No DCF
Making the Investment Decision
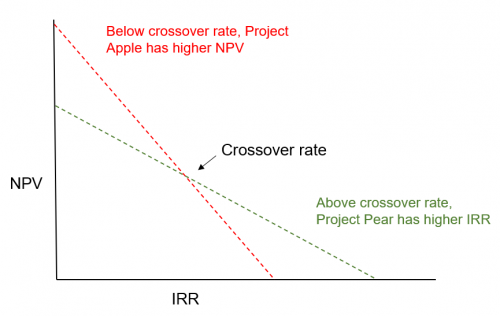
Sensitivity Analysis
The analysis of return (e.g. breakeven) is multiplied by the variance level (e.g. +- 15%) on both sides, to give worst, base and best case outcomes.
Financing Decision
Leverage
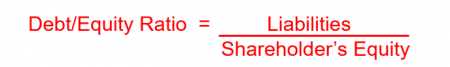
Higher debt/equity ratio indicates insolvency risk
However, if returns/earnings > Debt repayments, earnings will benefit from the debt.
