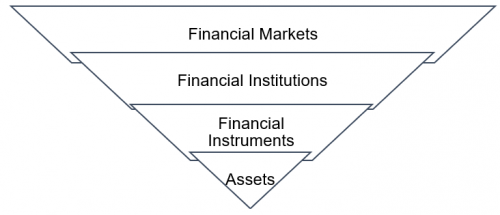
Financial Markets and Money
Money, as one type of financial asset, functions as:
- Medium of exchange
- Store of wealth
- Divisible
Types of Financial Institutions
Authorised deposit-taking institutions (commercial banks) | Government-licensed ADIs e.g. commercial banks |
Non-ADI financial institutions | Investment Banks – do not take deposits – they help companies raise capital |
Insurers and fund managers | Manage portfolios and risk |
Types of Financial Markets
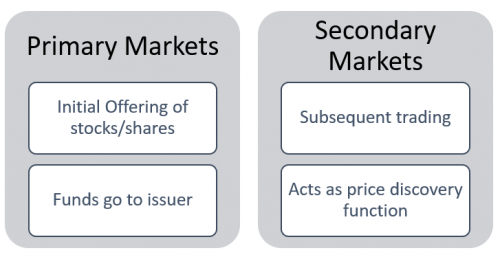
Retail and Wholesale Markets | |
Retail Markets | Direct flows of small amounts of funds between households, firms and intermediaries E.g. home loans |
Wholesale Markets | Large flows of funds between institutional lenders and borrowers E.g. Investment banks and IPOs |
Direct and Indirect Finance | |
Direct Finance | Direct between lender and borrower (often with help of broker) •Avoids costs of intermediation •However, costs of search and transaction costs (legal, advisory) incurred |
Indirect Finance | Finance undertaken through intermediary (e.g. bank) •Allows transformation and matching of assets and maturity •Economies of scale by spreading fixed costs •Risk management – intermediary exposed to borrower risk |
Off Balance Sheet transactions include: performance guarantees, underwriting, loan approvals, derivatives.
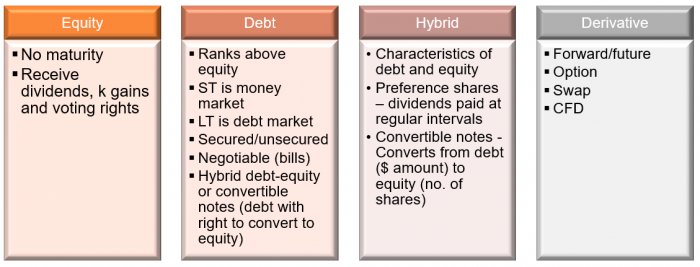
Types of Financial Instruments
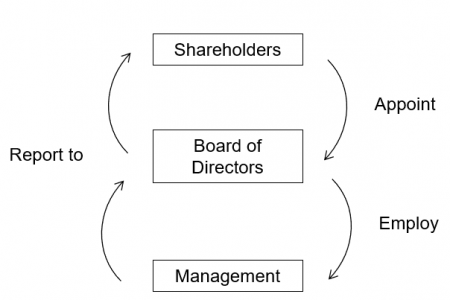
Corporate Governance