Balance of Payments
A nation’s balance of payments comprises the current account and capital account.
- The current account represents the net income / flow of money (like a P&L)
- The capital account represents changes in assets and liabilities (like a balance sheet)
The Current Account balance and Capital Account balance offset each other
i.e. CAB = – KAB
i.e. CAB = – KAB
Capital Flows
Current Account | Net income (short-term)
|
Capital & Financial Account | Net investment and financing
|
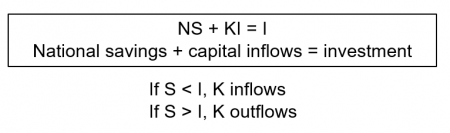
Current Account and Savings/Investment
- In a closed economy, S = I
- In an economy open to world trade, net capital inflows make up the difference
- If the trade balance (exports less imports) is positive, i.e. surplus, the country is a net lender (financing needed to overseas buyers) so there are net capital outflows.